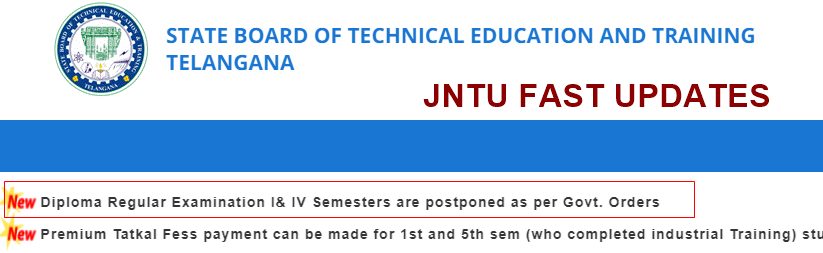
TS SBTET Diploma I & IV Semesters Regular Exams are Postponed

Telangana SBTET Diploma Regular Examination I& IV Semesters are postponed as per Govt. Orders.
Official website: https://exams.sbtet.telangana.gov.in/
TS SBTET Diploma I & IV Semesters Regular Exams are Postponed

Telangana SBTET Diploma Regular Examination I& IV Semesters are postponed as per Govt. Orders.

Official website: https://exams.sbtet.telangana.gov.in/
All the examinations will be conducted as per the schedule which has been already announced by the University.

All the chief superintendents/ Principals are request to conduct the examinations by strictly following the covid-19 guidelines as per the UGC and state government such as social distancing, wearing mask, thermal screening and sanitization of classrooms and parmises of examination centres.

Download the Official Notification here: Click Here
OU All the Exams will be conducted as per the schedule Only

OU All the examinations will be conducted as per the schedule by following COVID-19 protocols to save the academic year.

Download the Official Notification Here: Click Here
Telangana Schools, Colleges Will be Closed from 24th March Due to Coivid Until Further Orders

All educational institutions including schools and colleges have been ordered to shut in Telangana, amid a spike in COVID-19 cases.
The order comes into effect from March 24 onward till further directions. However, medical colleges will remain open.
Education minister Sabitha Indra Reddy said this decision was taken in view of the spread of Covid and at the request of parents. Classes will be held online.
తెలంగాణలో విద్యాసంస్థలు బంద్
తెలంగాణలో కరోనా వ్యాప్తి పెరుగుతున్నందున రేపటి నుంచి అన్ని విద్యా సంస్ధలను తాత్కాలికంగా మూసివేస్తున్నట్లు విద్యాశాఖమంత్రి సబితా ఇంద్రారెడ్డి అసెంబ్లీలో ప్రకటించారు. రాష్ట్రంలోని వైద్య కళాశాలలు మినహాయించి.. అన్ని హాస్టళ్లు, గురుకుల విద్యాలయాలు, ప్రభుత్వ, ప్రైవేట్ విద్యాసంస్థలు మూసివేత.. యథావిథిగా ఆన్లైన్లో తరగతులు కొనసాగుతాయని తెలిపారు.
UPSC CDS 1 Result 2021 – Written Test Merit List & Cutoff Marks Category Wise: Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) Common Defence Service (CDS) I written test has been conducted on 7th February. The examination has been conducted in a large number of places across the nation. A large number of competitors have appeared for the UPSC CDS I written test as per the schedule. Aspirants who competed for UPSC CDS 1 examination on 7th February can soon download UPSC CDS I English answer key 2021 from the official website, upsc.gov.in. By visiting the UPSC portal, competitors can download UPSC CDS Answer Key for English, Maths, and General Knowledge. The answer key will be available for all sets A, B, C, D for each subject. Competitors can download and cross-check the answers with the attempted set to calculate the score. By estimating the score, aspirants can assess their score, rank, level of competition, and other aspects. After analyzing the UPSC CDS I answer sheet, candidates can wait for the result. UPSC will soon announce the result date on its official portal, upsc.gov.in. Aspirants who competed for the examination can stay checking the portal for more updates. The UPSC CDS I 2021 Result Date, Downloading process, and other important details explained here in this article.

Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) organizes various examinations to hire the suitable candidates into Indian Military Academy. The UPSC annually releases various notifications to hire the aspirants into Air Force Academy (AFA), Indian Military Academy (IMA), Indian Naval Academy (INA), and Officers Training Academy (OTA). The organization recently announced the recruitment notification to hire candidates for Common Defence Service (CDS) II Posts for Indian Military Academy, Dehradun; Indian Naval Academy, Ezhimala, Kerala and Air Force Academy, Hyderabad (Pre-Flying) Training Course. The notification has been announced for 345 posts. The organization accepted applications from eligible and interested aspirants. Candidates aspiring to get UPSC CDS posts have applied for the announced posts within the application dates. Candidates will be shortlisted through the written test, interview rounds. Finally shortlisted candidates will be recruited in CDS I posts across the nation.
UPSC CDS 1 Result 2021, Selection List – Important Details
| Organization Name | Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) |
| Post Name | Combined Defence Services Exam I |
| Total Vacancies | 345 Posts |
| Exam Date | 7th February 2021 |
| Category | Result |
| Result Release Date | Released on 23rd March 2021 |
| Official Site | upsc.gov.in |
Download UPSC CDS I Result 2021, Qualified Candidates List @ upsc.gov.in
All the competitors who had competed for the CDS I written test round on 7th February can expect the results soon in the month of March [tentatively]. The result date is going to be announced shortly by the UPSC. Usually, UPSC will announce the results within one month after the examination. Hence the competitors can wait to check the result date from the UPSC portal, upsc.gov.in.
UPSC CDS I Cutoff Marks 2021
UPSC is going to announce the CDS 1 Cutoff marks along with the results. UPSC CDS I Category-wise cutoff marks will be announced for general, BC, SC, ST, and other categories. Candidates need to score the qualifying marks to clear the written test round. Candidates competed for the UPSC CDS I written test on 7th February can check the UPSC CDS I Qualifying Marks [previous year] from the following table.
Download UPSC CDS 1 Result, Merit List, and cutoff Marks 2021 – Available Now
CDS (I) 2018 Cut off
| Academy | Written Exam Cutoff | Final Cutoff |
| IMA | 118 | 240 |
| AFA | 138 | 279 |
| INA | 98 | 225 |
| OTA (Women) | 69 | 150 |
| OTA (Men) | 69 | 154 |
UPSC CDS I Merit List 2021
The UPSC releases the CDS I merit list 2021 with the names of qualified candidates. Candidate’s names who acquires the specified qualifying marks in the written test round will be mentioned in the merit list. UPSC CDS I 2021 merit list will be accessible to download along with the result. Competitors can check UPSC CDS I Merit List 2021 from the official website, upsc.gov.in.
Selected candidates will be recruited in,
Required Certificates
Shortlisted candidates have to submit the original certificates in support of educational qualifications, NCC (C) (Army Wing/Senior Division Air Wing/Naval Wing), age (Date of Birth), etc. along with attested copies in the following addresses.
If you have selected IMA/ SSC at first place to Army Headquarters,
A.G.’s Branch/Rtg./CDSE Entry Section for males and SSC Women Entry Section for women candidates, West Block-III, Ground Floor, Wing 1, R.K. Puram, New Delhi- 110066
If you have selected Navy
IHQ of MoD (Navy), DMPR (OI & R Section), Room No. 204, ‘C’-Wing, Sena Bhawan, New Delhi-110011
If you have selected Air Force at first place
PO 3 (A) Air Headquarters, ‘J’ Block, Room No. 17, Opp. Vayu Bhawan, Motilal Nehru Marg, New Delhi-110011
UPSC CDS 1 Important Dates 2021
| Events | CDS 1 Date |
| Combined Defence Services Examination (I) 2021 | February 7, 2021 |
| UPSC CDS 1 2021 Result Date | 23rd March |
| Submit DAF Dates | 3rd week of April 2021 |
| Date of commencement of Personal Interview | April/ May 2021 |
| Declaration of Final UPSC CDS 2021 Result | First week of November 2021 |
Steps to download UPSC CDS 1 Result 2021
AU Postponement of UG/PG and Professional Exams Scheduled on 26-03-2021

The examinations of Under Graduate / Post Graduate and Professional Courses scheduled to be held on 26th March, 2021 will rescheduled as follows in view Of Bharath Bandh Call given by Farmers.
| S.NO | COURSES | RESCHEDULED |
| 1 | ALL PG & PROFESSIONAL COURSES | 28TH MARCH, 2021 (SUNDAY) |
| 2 | ALL UG COUSES | 4TH APRIL, 2021 (SUNDAY) |
Download the Official Notification Here: Click Here
JKBOSE 10th Admit Card 2021: Jammu and Kashmir Board of School Education (JKBOSE) is all set to conduct the academic examinations for class 10th in the months of 3rd to 24th April 2021. Recently, JKBOSE has released the date sheet for the 10th Class academic examinations 2020-21. Students who are going to appear for JKBOSE 10th exams can go through the exam time table from the official portal, jkbose.jk.gov.in. All the students can get their hall tickets by visiting the JKBOSE website. Hall ticket/call letter is the most important document that is needed to carry to the examinations every day. Hence all the students are informed to download JK 10th Hall ticket 2021 as soon as the link activated on the website and carry it to the examination. Download admit cards, take a printout of the admit cards and keep it safe to carry to the examination. The invigilator will allow the students to proceed with the examination only after verifying the hall ticket of the candidate. Hence do not forget to carry the call letter to the examination.

Jammu and Kashmir State Board of School Education (JKBOSE) is the state level education board that was established in 1975. JKBOSE offers education for secondary and higher secondary classes in the state. The board monitors the education, syllabus and examination process for the secondary and higher secondary courses. It annually organizes the examinations in February/March months and releases the results in April/May months. Yearly, lakhs of students pursuing education from the board appears for the academic examinations as per the scheduled dates. The JKBOSE board is ahead to conduct the class 10th and 12th examinations in March month. Hence students can get ready for the examinations with good preparation.
JKBOSE 10th Admit Card 2021 – Important Details
| Name of the Board | Jammu and Kashmir State Board of School Education (JKBOSE) |
| Official Website | jkbose.jk.gov.in |
| Name of the Examinations | Jammu and Kashmir 10th Class Exams 2021 |
| Category | Hall ticket |
| Status | Released |
All the students going to appear for the JK 10th Class academic examinations 2020-21 can download the hall tickets from the JKBOSE official website, Jkbose.jk.gov.in. The hall ticket/admit card is going are released in march. Hence students pursuing 10th class under the JK Education Board can get ready to download the hall tickets. The hall ticket release date will be announced by the JKBOSE before the exams. Hence students can stay checking the JKBOSE portal for the latest updates.
The hall ticket/admit card must be taken to the examination without fail. If the candidate fails to carry the admit card, he/she will not be allowed to attend the test. Hence to overcome this trouble all the students are informed to carry the admit cards as a must. Students can download JK 10th Hall ticket 2021 before 10 days of the examination (approximately). After downloading the hall tickets, students can check the details of,
Go through the admit cards clearly after downloading. If any printing mistakes appear in name, sir name, date of birth or any other field, students can complain to the corresponding schools in which they are studying.
Download Jammu & Kashmir 10th Class Admit Cards 2021 – Available Now

JNTUK R16 4-2 Prestressed Concrete Material/Notes PDF Download
Students those who are studying JNTUK R16 Civil Branch, Can Download Unit wise R16 4-2 Prestressed Concrete Material/Notes PDFs below.

OBJECTIVES:
UNIT-1
Basic concepts of Prestressing- Advantages and Applications of Prestressed Concretes, High Strength Concrete- Permissible Stresses, Shrinkage, Creep, Deformation Characteristics, High strength Steel- Types, Strength- Permissible Stresses- Relaxation of Stress, Cover Requirements.
UNIT-2
Prestressing Systems- Introduction, Tensioning devices, Pre-tensioning Systems, Post tensioning Systems, Basic Assumptions in Analysis of prestress and design, Analysis of prestress, Resultant Stresses at a section- pressure line- Concepts of load balancing- Stresses in Tendons, Cracking moment.
UNIT-3
Losses of Pre-stressing- Loss of Pre-stress in pre-tensioned and post tensioned members due to various causes -Elastic shortening of concrete, shrinkage of concrete, creep of concrete, Relaxation stress in steel, slip in anchorage, differential shrinkage- bending of members and frictional losses- Total losses allowed for design
UNIT-4
Design for Flexural resistance- Types of flexural failure – Code proceduresDesign of sections for flexure- Control of deflections- Factors influencing DeflectionPrediction of short term and long term deflections.
UNIT-5
Design for Shear and Torsion- Shear and Principal Stresses- Design of Shear reinforcements- Codal Provisions- Design for Torsion, Design for Combined bending, shear and torsion.
UNIT-6
Transfer of Prestress in pre tensioned members- Transmission length- Bond stresses- end zone reinforcement- Codal provisions- Anchorage zone Stresses in Post tensioned members- Stress distribution in end block- Anchorage Zone reinforcement.
TEXT BOOKS:
REFERENCE BOOKS:
OUTCOMES:
DTE Karnataka Time Table April/May 2021 Download Course Wise PDF : DTE, Karnataka has released the BTELINX Diploma Time Table 2021 for st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th Sem examinations. Students pursuing under DTE Karnataka can check the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th sem Diploma exam schedule from the official portal, dte.kar.nic.in. The DTE Karnataka released the time table for 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th semesters. The even semester examinations will be conducted for the students in April/May months. While the odd semester examinations will be held in November and December months actually. but due to covid 19 it is getting delay. Hence aspirants presently undergoing the odd semesters can check the DTE Karnataka time table 2021.
Department of Technical Education Karnataka is the state level technical university works specially to offer the technical courses for the aspirants. It offers affiliation to various technical colleges across the Karnataka state. The board offers diploma, ITI and various other technical courses for the students. Annually a huge number of students are coming out of this board with certification. Many of the Government/private/aided colleges in the state of Karnataka are affiliated with this board. Lakhs of students annually coming out of this university annually. Students who are pursuing under DTE Karnataka can download DTE Karnataka BTELinx time table 2021 for 1st, 3rd, 5th semesters from the official website.

BTELINX Diploma Exam Time Table 2021
| Name of the University | Department of Technical Education Karnataka |
| Name of the Exam | Diploma Examinations 2021 |
| Start of Odd semester exams | April/May 2021 |
| Declaration Type | DTE Karnataka Diploma Time Table 2021 |
| Time Table Release Status | Released Course Wise |
| Official Website | dte.kar.nic.in |
DTE Karnataka BTELINX time table 2021 is accessible to download on official website. All the students can download diploma time table for 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semesters from official website. Go through it carefully to check the regular and practical examination dates.
April/May 2021 Theory exams Provisional Time table
DTE Karnataka Diploma Provisional Time Table April/May 2021 – Available Now
| Sl.No. | Course Code | Course name |
| 1 | AE | Aeronautical Engineering |
| 2 | AG | Agricultural Engineering |
| 3 | FT | Apparel Design & Fabrication Technology |
| 4 | AR | Architecture |
| 5 | AT | Automobile Engineering |
| 6 | CR | Ceramics Engineering |
| 7 | CH | Chemical Engineering |
| 8 | CN | Cinematography |
| 9 | CE | Civil Engineering (General) |
| 10 | CD | Civil Engineering.(D’Ship) |
| 11 | EN | Civil(Environmental) Engineering |
| 12 | PH | Civl Engineering (Public Health Engg) |
| 13 | CP | Commercial Practice |
| 14 | CS | Computer Science & Engineering |
| 15 | EE | Electrical & Electronics Engineering |
| 16 | EC | Electronics & Communication Engineering |
| 17 | EI | Electronics Instrumentation & Control Engineering |
| 18 | IS | Information Science & Engineering |
| 19 | ID | Interior Decoration |
| 20 | LT | Leather & Fashion Technology |
| 21 | LB | Library Science and Information Management |
| 22 | ME | Mechanical Engineering (General) |
| 23 | HP | Mechanical Engineering (HPT) |
| 24 | WS | Mechanical Engineering (WSM) |
| 25 | MY | Mechanical Engineering (MTT) |
| 26 | MI | Mechanical Engineering (Instrumentation) |
| 27 | MC | Mechatronics Engineering |
| 28 | MT | Metallurgy Engineering |
| 29 | MN | Mining Engineering |
| 30 | MM | Modern Office Management |
| 31 | PO | Polymer Technology |
| 32 | PT | Printing Technology |
| 33 | SR | Sound Recording Engineering |
| 34 | TX | Textile Engineering |
| 35 | WH | Water Technology and Health Science |
| 36 | TD | Tool and Die Making |
Yes, Time table PDF is available for Download.
Starts from april and ends in May 2021.
We have uploaded provisional time table in the above post. Just click on link and download and search your course datesheet.
JNTUK B.Tech 4-2 R16 Civil Materials: Students Can Download JNTUK 4-2 Civil Engineering R16 Regulation Materials/ E Note Books / Text Books Subject Wise From Below.

Students of Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada can avail of B.Tech 4-2 can avail of the materials for R16 regulation for various branches. Students can download JNTUK B.Tech 4-2 Sem R16 Civil Materials Subject Wise PDF from the links provided here. By tapping on the link, one can download materials for JNTUK 4-2 Sem Civil R16. The electronics and communication engineering Students can download the subject-wise materials PDFs collected from various sources. By referring to the materials one can gain knowledge to clear the exams with a good score. The course materials include Estimation Specification & Contracts, Construction Technology & Management, Prestressed Concrete and various other Civil related books of various popular authors. Check the following B.Tech R16 Civil 4-2 Materials PDFs and download them for free.
JNTUK B.Tech 4-2 Sem R16 Civil Course Structure:
| S. No. | Subjects | L | T | P | Credits |
| 1 | Estimation Specification & Contracts | 4 | — | — | 3 |
| 2 | Construction Technology & Management | 4 | — | — | 3 |
| 3 | Prestressed Concrete | 4 | — | — | 3 |
| 4 | Elective III i. Bridge Engineering ii. Soil Dynamics and Foundations iii. Solid and Hazardous Waste Management iv. Water Resources Systems Planning v. Urban Transportation Planning Engg | 4 | — | — | 3 |
| 5 | Seminar on Internship Project | — | 3 | — | 2 |
| 6 | Project | — | — | — | 10 |
| Total Credits | 24 |
Also Check: JNTUK 4-2 Sem R16 Civil Syllabus
Students who are pursuing the B.Tech 4-2 Civil R16 Regulation can check the text books, reference books, and e-resourses provided here for free. Students can get the complete chapter-wise information from their respective text books. And from the following information from the e-resourses, text books from the familer authors will provide the extra knowledge and understanding of each subject. Hence ts helps to score good in exams. Here we have collaboratively given the best JNTUK 4-2 R16 Civil materials at one place for the reference of students.
Estimation Specification & Contracts Material
Construction Technology & Management Material
Elective III
i. Bridge Engineering Material
ii. Soil Dynamics and Foundations Material
iii. Solid and Hazardous Waste Management Material
iv. Water Resources Systems Planning Material
v. Urban Transportation Planning Engg Material